Hearing Loss Prevention

Eating Habits and Hearing Loss Recent research has shown that nutrition can slow the loss of hearing due to aging. According to the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, “If you eat two servings of (fresh) fish, you lower the risk of hearing loss by 42 percent if you’re 50 years old or older.” Eating fish…
How to Purchase Hearing Instruments

7 Questions You Should Ask Hearing Professionals Before Making an Appointment Are you an audiologist? Audiologists hold advanced degrees from accredited universities and have special training in the identification, assessment and non-medical treatment of hearing disorders. They must complete a full-time internship, pass a demanding national examination and be licensed by the state. The only…
What Drugs Can Cause Hearing Loss?

According to the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association, there are currently more than 200 chemicals and medications that may result in hearing and balance disorders. Ototoxic is the term health professionals use for medications and supplements that produce hearing loss as a side effect. Some physician-prescribed medications can damage the delicate hair cells in the inner ear…
Hearing Loss and Listening Fatigue

The stresses of everyday life can test your endurance and patience. If, at the end of the day, you feel more exhausted than you think is appropriate, it might be time to schedule a recheck of your hearing. You may have listening fatigue, a condition caused by the increased effort you’re exerting to listen and…
Common Medical Conditions & Hearing Loss
Many medical conditions can contribute to hearing loss. Below are some of the most common. Diabetes As you know, diabetes is one of the most prevalent health problems today. An estimated 30 million people in the United States are afflicted with diabetes, while another 86 million are pre-diabetic. Many physicians, however, are unaware that damage…
Reading Your Audiogram
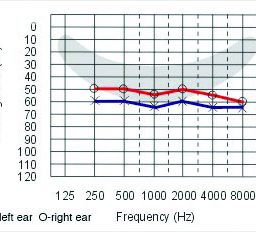
The basic hearing examination is a measure of the softest sounds your ears can perceive, also called the threshold of hearing. Understanding Your Audiogram The audiogram is a graphic display of these hearing thresholds that paints a picture of your hearing ability. All test results are graphed on the audiogram, with frequency (pitch) increasing from…
Earwax Coning and Cleaning

The function of earwax is simple. It provides a barrier from external contaminants, lubricates the ear canal and its acidic nature wards off fungal infections. Many of my new patients believe that excessive earwax is the cause of their hearing loss. Truth be told, accumulated earwax is almost never the problem. Most hearing loss is…
Your Brain & Hearing
Did you know that your brain is plastic? I’m not speaking of the substance that we see every day in products from automobiles to hearing aids. Rather, I’m referring to your “neuroplastic” brain. This term means that the brain reorganizes itself when auditory input is reduced due to untreated hearing loss. The brains of people…
Your Hearing Ability
Your hearing ability is the direct result of the interaction between two systems: the ears and the brain. Your ears are encoding devices. Thousands of microscopic sensory nerves sense sounds and turn these sounds into electrical signals. These signals are decoded and given meaning by the brain. Many who have long-standing hearing losses perceive sound differently than those…
What is Noise Induced Hearing Loss?

Noise induced hearing loss is the second most common form of hearing loss (ranking behind presbycusis, hearing loss related to normal aging), and is the most preventable type. How Can Sounds Hurt Your Ears? Background sound is a constant in our busy lives. Normally, background noises are at safe levels that won’t impact our hearing….

